On November 16, 2018, Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) 2017/2018 China Report was launched during the G20 Entrepreneurship Roundtable 2018 in Xiamen, China. The report states, the most active entrepreneurs in China are young people between the age of 25 and 34. The trend also shows that the proportion of entrepreneurs with higher education background and income levels have increased over the years.

Jointly published by the Entrepreneurship Research Center on G20 Economies and TusPark Research Institute for Innovation, the report is the 15th GEM China research report since 2002. Based on the annual survey data of the past 15 years, the report analyzed the development and changes of Chinese entrepreneurial activities from four aspects: structure, quality, entrepreneurial ecosystem and regional disparities.
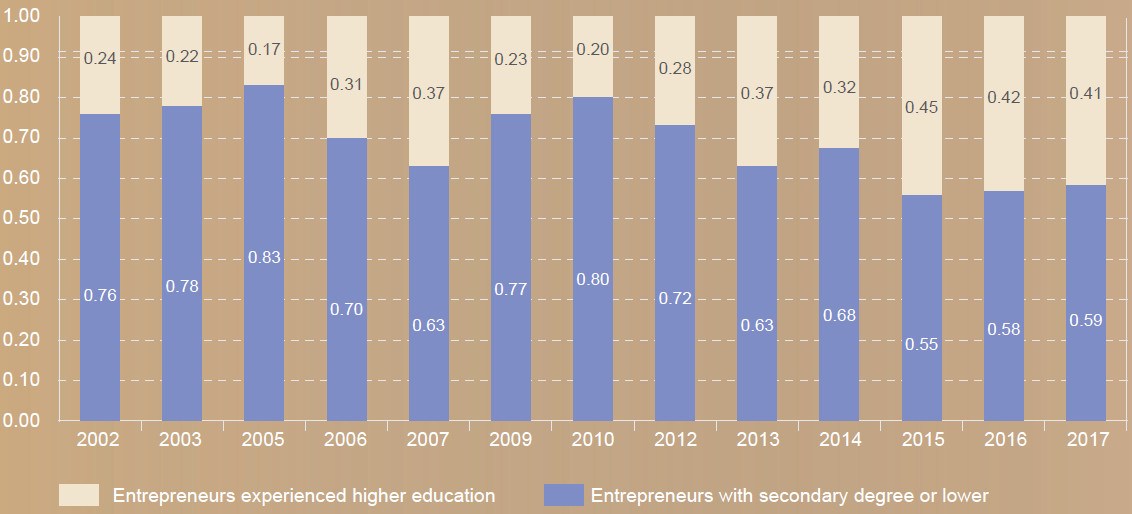
The report shows that the most active group of entrepreneurs in China is young people aged from 25 to 34, accounting for more than 30% of the total number of entrepreneurs. More than 60% of the entrepreneurs are opportunity-driven and this proportion continues to grow. In the 15 years from 2002 to 2017, the proportion of entrepreneurs with low educational background has gradually decreased while the proportion of entrepreneurs with high educational attainment and high-income levels has increased. Most entrepreneurs choose to start businesses in the customer service industry which is dominated by wholesale or retail. The proportion of entrepreneurs in knowledge-based service industries remains low.
The proportion of business discontinuation has decreased over the years, from 8% in 2003 to 2% in 2017. Fewer entrepreneurs believe they have the required skills and knowledge to start up; while only 25% of the entrepreneurs feared of failure back in 2002, the percentage has now increased till 41%. A probable reason for the phenomenon is that the entrepreneurial skills required for a successful business have increased over the years due to technological growth and social development, and more entrepreneurs are more aware of their shortcomings.
According to the report, the capability of job creation has been increasing. The proportion of high growth startup companies in China ranked above the average of G20 economies. Even though the quality of entrepreneurial activities in China has increased over the past 15 years, there remains a gap between China and the developed G20 countries in terms of innovation capability and high-tech entrepreneurship ratio.
China's entrepreneurial ecosystem has been continuously improving. Physical infrastructure, market openness, as well as culture and social norms are three aspects Chinese entrepreneurial ecosystem have been doing well in. However, more needs to be done in the aspects of commercial infrastructure, R&D transfer, as well as education and training. Data indicates that the active level of entrepreneurship in urban and rural areas have been relatively balanced in the past years, but the proportion of opportunity-driven startup is higher in the cities. Regional disparity in entrepreneurial activities has not shown significant decrease.